
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{x^{2016}+x-2}{\sqrt{2018x+1}-\sqrt{x+2018}}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{2016x^{2015}+1}{\frac{1009}{\sqrt{2018x+1}}-\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x+2018}}}=\frac{2017}{\frac{1009}{\sqrt{2019}}-\frac{1}{2\sqrt{2019}}}=2\sqrt{2019}\)
Để hàm liên tục tại \(x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}f\left(x\right)=f\left(1\right)\Rightarrow k=2\sqrt{2019}\)
2.
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{x^2+ax+b}{x^2-1}=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b+1=0\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{2x+a}{2x}=\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=-1\\\frac{a+2}{2}=\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-1\\b=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow S=1\)
3.
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\sqrt{x^2+x+2}-2+2-\sqrt[3]{7x+1}}{\sqrt{2}\left(x-1\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\sqrt{x^2+x+2}+2}-\frac{7\left(x-1\right)}{\sqrt[3]{\left(7x+1\right)^2}+2\sqrt[3]{7x+1}+4}}{\sqrt{2}\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+x+2}+2}-\frac{7}{\sqrt[3]{\left(7x+1\right)^2}+2\sqrt[3]{7x+1}+4}\right)\)
\(=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\frac{3}{4}-\frac{7}{12}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b+c=1+12+0=13\)

Chọn A.
Với x = 1 ta có f(1) = k2
Với x ≠ 1 ta có
![]()
suy ra ![]() .
.
Vậy để hàm số gián đoạn tại x = 1 khi ![]() ⇔ k2 ≠ 4 ⇔ k ≠ ±2.
⇔ k2 ≠ 4 ⇔ k ≠ ±2.

- TXĐ: D = R.
+ Với x = 1 ta có f ( 1 ) = k 2
+ Với x ≠ 1 ta có:
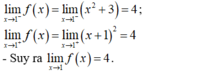
- Vậy để hàm số gián đoạn tại x = 1 khi và chỉ khi:
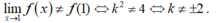
Chọn A

Nhìn thấy đạo hàm bằng định nghĩa là thấy ớn, dài dữ dội
- Khi \(x>1\) \(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\frac{4x-4}{x+1}\)
\(\Delta x=x-x_0\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta y=\frac{4\Delta x+4x_0-4}{x_0+\Delta x+1}-\frac{4x_0-4}{x_0+1}=\frac{8\Delta x}{\left(x_0+1\right)\left(x_0+1+\Delta x\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x_0\right)=\lim\limits_{\Delta x\rightarrow0}\frac{8\Delta x}{\Delta x\left(x_0+1\right)\left(x_0+1+\Delta x\right)}=\frac{8}{\left(x_0+1\right)^2}\)
- Khi \(x< 1\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=2x-2\)
\(\Delta x\) là số gia của \(x_0< 1\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta y=2\left(x_0+\Delta x\right)-2-\left(2x_0-2\right)=2\Delta x\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x_0\right)=\lim\limits_{\Delta x\rightarrow0}\frac{2\Delta x}{\Delta x}=2\)
- Khi \(x\rightarrow1^+\Rightarrow\Delta y\rightarrow2\left(1+\Delta x\right)-2\rightarrow2\Delta x\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f'\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{\Delta x\rightarrow0}\frac{2\Delta x}{\Delta x}=2\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}f'\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\frac{8}{\left(1+1\right)^2}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=2\)

2: ĐKXĐ: x<>1
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(x^2-3x+3\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-5x+3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
f'(x)=0
=>x^2-2x=0
=>x(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1:
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-2\sqrt{2}\cdot x^2+8x-1\)
=>\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-2\sqrt{2}\cdot2x+8=x^2-4\sqrt{2}\cdot x+8=\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2\)
f'(x)=0
=>\(\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2=0\)
=>\(x-2\sqrt{2}=0\)
=>\(x=2\sqrt{2}\)