Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải của bạn Nhật Linh đúng rồi, tuy nhiên cần thêm điều kiện để A có nghĩa: \(x\ne\pm2\)

a)
2x-3=0 => x=3/2
b)
2x^2 +1 =0 => vô nghiệm
c) x^2 -25 =0 => x=5 loiaj
x=-5 nhân
d)
x^2 -25 =0 => x=5 loại
x=-5 loại

Câu trả lời sai là:
(C) Giá trị của Q tại \(x=3\) là \(\dfrac{3-3}{3+3}=0\)
Do ĐKXĐ của phương trình
\(Q=\dfrac{x^2-6x+9}{x^2-9}\) là \(x\ne\pm3\)

1/ a, \(A=\dfrac{3}{2x+6}-\dfrac{x-6}{2x^2+6x}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x-6}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-x+6}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+6}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x+3\right)}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
Vậy \(A=x\)
b/ Khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{2}}=2\)
Vậy...
2/a,
\(A=\dfrac{5x+2}{3x^2+2x}+\dfrac{-2}{3x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x+2}{x\left(3x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{x\left(3x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x+2-2x}{x\left(3x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+2}{x\left(3x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
Vậy....
b/ Với \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{3}}=3\)
Vậy..

a)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ne0\\x+2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
x khác 1
c)
x khác 0; x khác 5
d) x khác 5 ; x khác -5

1.
a) \(x\left(x+4\right)+x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(x\left(x-3\right)+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1:
a, \(x\left(x+4\right)+x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+4\right)+\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=-4\) hoặc \(x=-1\)
b, \(x\left(x-3\right)+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=3\) hoặc \(x=-2\)

a) giải phương trình
\(\dfrac{2x^2-3x-2^{ }}{_{ }x^2-4}\) = 2
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2-3x-2}{x^2-4}\) = \(\dfrac{2\left(x^2-4\right)}{x^2-4}\)
=>2x2 - 3x - 2 = 2(x2 - 4)
<=>2x2 -3x - 2 = 2x2 - 8
<=>2x2 - 2x2 - 3x = -8 + 2
<=>-3x = -6
<=> x = 2
Vậy không tồn tại giá trị nào của x thỏa mãn điều kiện của bài toán
b) Ta phải giải phương trình
\(\dfrac{6x-1}{3x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{2x+5}{x-3}\)
=>x = \(\dfrac{-7}{38}\)
c) Ta phải giải phương trình
\(\dfrac{y+5}{y-1}\) - \(\dfrac{y+1}{y-3}\) = \(\dfrac{-8}{\left(y-1\right)\left(y+1\right)}\)
không tồn tại giá trị nào của y thỏa mãn điều kiện của bài toán
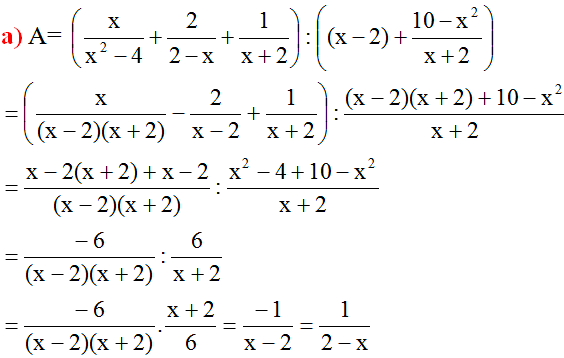
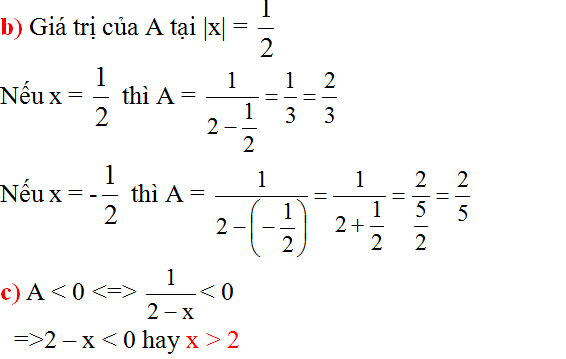



\(\dfrac{x}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{2x+4}{4-x^2}\\ =\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-2x+2x+4-2x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x}{x+2}\)
\(\left|x+1\right|=3\\ \left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=3\\x+1=-3\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(loai\right)\\x=-4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
với x=-4 thì
\(\dfrac{-4}{-4+2}=\dfrac{-4}{-2}=2\)
\(=>P=\dfrac{x}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{-2x-4}{x^2-4}\)`(x ne +-2)`
\(P=\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{-2x-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2-2x+2x+4-2x-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x}{x+2}\)
`|x+1| =3`
`=>[(x+1=3),(x+1=-3):}`
`=> [(x=3-1=2(ktm) ),(x=-3-1=-4(t/m)):}`
Thay `x=-4` vào `P` ta đc
`P= (-4)/(-4+2) = 2`