
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,đk\left(B\right):x\ne\pm3\\ B=\dfrac{3}{x-3}-\dfrac{6x}{9-x^2}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\\ =\dfrac{3}{x-3}+\dfrac{6x}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\\ =\dfrac{3\left(x+3\right)+6x+x\left(x-3\right)}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{3x+9+6x+x^2-3x}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}\)
\(b,P=A.B\\ =\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}\times\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}\\ =\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}\)
\(c,\) Để P nguyên
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}=1+\dfrac{4}{x-3}\)
=> \(x-3\inƯ\left(4\right)\)
\(Ư\left(4\right)=\left\{-1;1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
\(=>x=\left\{2;4;5;1;7;-1\right\}\)

a: Thay x=-4 vào B, ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{-4+3}{-4}=\dfrac{-1}{-4}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
b: \(P=A\cdot B=\dfrac{x^2-3x+2x-9+3x+9}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+3}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{\left(x-3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
c: Để P nguyên thì \(x-3\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{4;2;8;-2\right\}\)

Answer:
a) \(\frac{5x}{2x+2}+1=\frac{6}{x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{5x}{2\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{12}{2\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x+2x+2-12=0\)
\(\Rightarrow7x-10=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{10}{7}\)
b) \(\frac{x^2-6}{x}=x+\frac{3}{2}\left(ĐK:x\ne0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-6=x^2+\frac{3}{2}x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3}{2}x=-6\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-4\)
c) \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\ge\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3\left(3x-2\right)-2\left(3x+3\right)}{12}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow9x-6-6x-6\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-12\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\ge4\)
d) \(\left(x+1\right)^2< \left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+2x+1< x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow4x< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow x< 0\)
e) \(\frac{2x-3}{35}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\le\frac{x^2}{7}-\frac{2x-3}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x-3+5\left(x^2-2x\right)}{35}\le\frac{5x^2-7\left(2x-3\right)}{35}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-3+5x^2-10x\le5x^2-14x+21\)
\(\Rightarrow6x\le24\)
\(\Rightarrow x\le4\)
f) \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\le\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3\left(3x-2\right)-2\left(3x+3\right)}{12}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow9x-6-6x-6\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x\le12\)
\(\Rightarrow x\le4\)

Bài 1:
a) \(A=5\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+\left(2x+3\right)^2\)
\(A=5\left(x^2-3^2\right)+\left(4x^2+12x+9\right)\)
\(A=5x^2-45+4x^2+12x+9\)
\(A=9x^2+12x-36\)
b) Thay x = 1/3 vào A ta có :
\(A=9\cdot\frac{1}{9}+\frac{12}{3}-36\)
\(A=1+4-36\)
\(A=-31\)
a) cho x+y=1. Tính giá trị biểu thức x^3+ y^3+ 3xy
b) cho x-y=1. Tính giá trị biểu thức x^3- y^3- 3xy

x^3+ y^3+ 3xy
=(x+y)(x^2 -xy + y^2 ) + 3xy
=x^2 -xy + y^2 + 3xy
=x^2 + 2xy + y^2
=(x+y)^2 =1
=> x^3+ y^3+ 3xy=1

a, \(A=3x^3\left(x^5-y^5\right)+y^5\left(3x^3-y^3\right)\\ =3x^8-3x^3y^5+3x^3y^5-y^8\\ =3x^8-y^8\)
b, Có \(y^4=x^4\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow y^8=3x^8\)
Thay vào A, ta được: \(A=3x^8-3x^8=0.\)

a) do gt của bt 3-4x lớn hơn gt của bt 2(3-x)
=> 3-4x>2(3-x)
⇔ 3-4x>6-2x
⇔ 3-6>4x-2x
⇔-3>2x
⇔ 2x<-3
⇔ x< \(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
vậy x< \(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
b vì gt của bt \(\dfrac{3-1}{2}\) ko lớn hơn gt của bt x+2
=> \(\dfrac{3-1}{2}\ge x+2\)
⇔ 1>x+2
⇔ -1>x
vậy x<-1
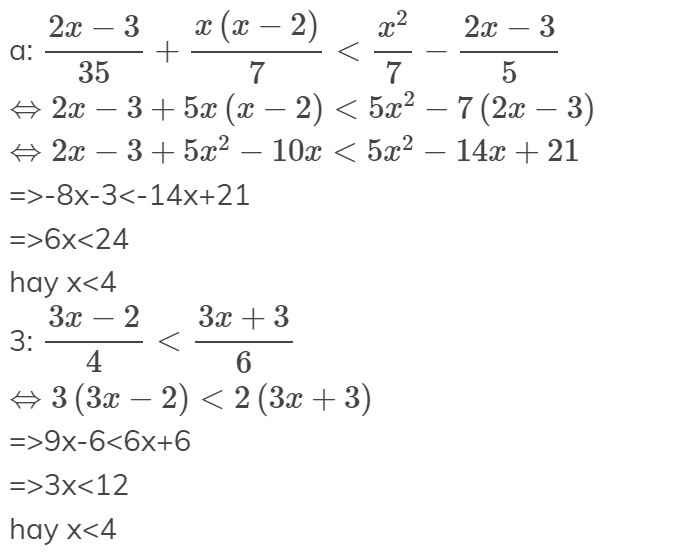
3/3-x=0
3/3-3x/3=0
3-3x=0
-3x=-3
x=-3/-3
x=1
tìm x nguyên để bth nguyên hả bạn ?
\(3-x\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)