
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


(2x2 + 1)(x-3)=0
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2+1=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2=-1\Rightarrow x^2=-\frac{1}{2}\left(vl\right)\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x=3
48-(15-x)5=48
(15-x)5=48-48
(15-x)5=0
=> 15-x =0
x =15-0
x =15
Vậy x=15

(2x + 1) + (2x + 2) + ... + (2x + 2015) = 0
=> 2015.2x + (1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 2015) = 0
=> 4030x + (2015 + 1).2015 : 2 = 0
=> 4030x = -2031120
=> x = -504
(2x+1)+(2x+2)+...........+(2x+2015)=0
2x .2015+(1+2+3+...............2015)=0
4030x + 2031120 =0
4030x =0-2031120
4030x = -2031120
x = -2031120:4030
x = -504

\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{2.4}+\dfrac{2}{4.6}+...+\dfrac{2}{\left(2x-2\right).2x}=\dfrac{11}{24}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4-2}{2.4}+\dfrac{6-4}{4.6}+...+\dfrac{2x-\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(2x-2\right).2x}=\dfrac{11}{24}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{6}+...+\dfrac{1}{2x-2}-\dfrac{1}{2x}=\dfrac{11}{24}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2x}=\dfrac{11}{24}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2x}=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{11}{24}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2x}=\dfrac{1}{24}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=24\)
\(\Rightarrow x=12\)

a) \(2^x=8.64=2^3.2^6=2^9\Rightarrow x=9\)
b) \(3.2^x=48\Rightarrow2^x=16=2^4\Rightarrow x=4\)

a, 36:(x–5) = 2 2
(x–5) = 9
x = 14
b, [3.(70–x)+5]:2 = 46
[3.(70–x)+5] = 92
70–x = 29
x = 41
c, 450:[41–(2x–5)] = 3 2 .5
41–(2x–5) = 10
2x–5 = 31
2x = 36
x = 18
d, 230+[ 2 4 +(x–5)] = 315. 2018 0
16+(x–5) = 315–230
x–5 = 85–16
x = 69+5
x = 74
e, 2 x + 2 x + 1 = 48
2 x .(2+1) = 48
2 x = 16 = 2 4
x = 4
f, 3 x + 2 + 3 x = 2430
3 x . 3 2 + 1 = 2430
3 x = 2430:10 = 243 = 3 5
x = 5

1e) Để \(\frac{2x-1}{x-3}\) nguyên thì \(2x-1⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6+5⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-3\right)+5⋮x-3\)
Do \(2\left(x-3\right)⋮x-3\) \(\Rightarrow5⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\in\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2;2;4;8\right\}\)
Vậy:...................

Ta có : 2x - 2y = 48
=> x > y => x = y + n với n ∈ N*
=> 2x - 2y = 2y + n - 2y = 48
=> 2y . 2n - 2y = 48
=> 2y . (2n - 1) = 48
=> 2y ; 2n - 1 ∈ Ư(48) ∈ {1;2;3;4;6;8;12;16;24;48}
Mà 2n - 1 luôn lẻ với mọi n ∈ N*
=> 2n - 1 = 3
=> 2y . 3 = 48
=> 2y = 16 = 24
=> y = 4
=> 2x - 24 = 48
=> 2x = 48 + 16 = 64 = 26
=> x = 6
Vậy x = 6 ; y = 4
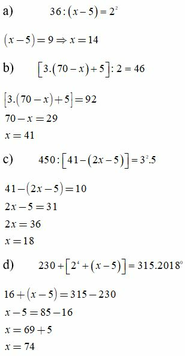
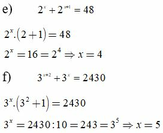
2x + 2 - 2x = 48
=> 2x . 22 - 2x = 48
=> 2x (22 - 1) = 48
=> 2x . 3 = 48
=> 2x = 16
=> 2x = 24
=> x = 4
\(2^{x+2}-2^x=48\)
\(2^x.2^2-2^x=48\)
\(2^x.\left(2^2-1\right)=48\)
\(2^x.3=48\Leftrightarrow2^x=16\)
\(2^x=16=2^4\)
Vậy x = 4