
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a.ĐKXĐ \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-3\\x\ne2\end{cases}}\)
A=\(\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{1}{x-2}\)
=\(\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-5-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=\(\frac{x-4}{x-2}\)
b. Để A >0 thì \(\frac{x-4}{x-2}\) >0 \(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x< 2\\x>4\end{cases}}\)
Kết hợp ĐK thì \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x< 2,x\ne-3\\x>4\end{cases}}\)
c. \(A=\frac{x-4}{x-2}=1+\frac{-2}{x-2}\)
Để A nguyên thì \(x-2\inƯ\left(-2\right)=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0,1,3,4\right\}\)
Khi thay vào A, để A dương thì \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\)
Vậy để A nguyên dương thì \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\)
Câu c, có thể nói kết hợp với điều kiện giải được trong câu b, ta tìm được \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\)

theo đề ta có: \(x+y+z=0\Rightarrow\left(x+y+z\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2+z^2+2\cdot\left(xy+yz+zx\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2+z^2=-2\left(xy+yz+xz\right)\left(1\right)\)
ta co: \(x^3+y^3+z^3-3xyz=\left(x+y+z\right)\left(x^2+y^2+z^2-xy-yz-xz\right)\)
mà x + y + z = 0
\(\Rightarrow x^3+y^3+z^3-3xyz=0\Rightarrow x^3+y^3+z^3=3xyz\left(2\right)\)
a. VT = \(\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)^2=x^4+y^4+z^4+2\cdot\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+x^2z^2\right)\)
ta có: \(\left(xy+yz+zx\right)^2=\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+x^2z^2\right)+2xyz\cdot\left(x+y+z\right)\)
vì x+y+z=0 nên: \(\left(xy+yz+zx\right)^2=\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+x^2z^2\right)\)
từ (1) ta có: \(\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)^2=\left\lbrack-2\left(xy+yz+zx\right)^{}\right\rbrack^2\) (*)
\(=4\cdot\left(xy+yz+zx\right)^2=4\cdot\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2\right)\)
ta có: \(4\cdot\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2\right)=x^4+y^4+z^4+2\cdot\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2\right)\)
mà: \(2\cdot\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2\right)=x^4+y^4+z^4\)
thay vào (*) ta được:
\(\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)^2=\left(x^4+y^4+z^4\right)+2\cdot\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2\right)\)
\(=x^4+y^4+z^4+x^4+y^4+z^4=2\cdot\left(x^4+y^4+z^4\right)=VP\)
⇒ đpcm
b. \(VT=5\cdot\left(x^3+y^3+z^3\right)\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\)
\(=5\cdot\left(3xyz\right)\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\)
\(=15xyz\cdot\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\) (3)
\(x+y+z=0\Rightarrow x+y=-z\)
\(x^5+y^5+z^5=x^5+y^5+\left\lbrack-\left(x+y\right)\right\rbrack^5=x^5+y^5-\left(x+y\right)^5\)
\(=x^5+y^5-\left(x^5+5y^4+10x^3y^2+10x^2y^3+5xy^4+y^5\right)\)
\(=-5x^4y-10x^3y^2-10x^2y^3-5xy^4\)
\(=-5xy\left(x^3+2x^2y+2xy^2+y^3\right)\)
\(=-5xy\left\lbrack x^3+y^3+2xy\left(x+y\right)\right\rbrack\)
\(=-5xy\left\lbrack\left(x+y\right)^3-3xy\left(x+Y\right)+2xy\left(x+y\right)\right\rbrack\)
\(=-5xy\left\lbrack\left(x+Y\right)^3-xy\left(x+y\right)\right\rbrack\)
\(=-5xy\left(x+Y\right)\left\lbrack\left(x+y\right)^2-xy\right\rbrack\)
vì x+y=-z nên ta có:
\(x^5+y^5+z^5=-5xy\left(-z\right)\left\lbrack\left(-z\right)^2-xy\right\rbrack=5xyz\left(x^2-zy\right)\)
mặt khác \(x+y=-z\Rightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2=z^2\Rightarrow x^2+y^2+2xy=z^2\)
\(x^2+y^2+z^2=x^2+y^2+\left(x+y\right)^2\)
\(=x^2+y^2+x^2+2xy+y^2=2\cdot\left(x^2+xy+y^2\right)\)
\(z^2-xy=\left(x+y\right)^2-xy=x^2+2xy+y^2-xy=x^2+xy+y^2\)
vậy \(x^5+y^5+z^5=5xyz\cdot\left(x^2+xy+y^2\right)=\frac52xyz\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2\cdot\left(x^5+y^5+z^5\right)=5xyz\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\)
⇒ \(6\cdot\left(x^5+y^5+z^5\right)=15xyz\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\) (4)
từ (3) và (4) ⇒ VT = VP

\(x+y+z=0\rArr\left(x+y+z\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2+z^2+2xy+2yz+2zx=0\)
\(\rArr x^2+y^2+z^2+2\left(xy+yz+xz\right)=0\)
\(\rArr x^2+y^2+z^2=0\) (do \(xy+yz+xz=0\) )
\(\rArr x=y=z=0\)
Do đó:
\(\left(x-1\right)^{2023}+y^{2024}+\left(z+1\right)^{2025}=\left(0-1\right)^{2023}+0^{2024}+\left(0+1\right)^{2025}=-1+0+1=0\)

đk: x khác -3; 2
b)\(A=\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{x+3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x^2-4-5-x-3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x-4}{x-2}\)
c) A=3/4 <=> \(\frac{x-4}{x-2}=\frac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow4x-16=3x-6\) tự giải pt này ra x nha
d) \(A=\frac{x-4}{x-2}=\frac{x-2-2}{x-2}=1-\frac{2}{x-2}\)=> A thuộc Z <=> 2/x-2 thuộc Z( 1 thuộc Z rồi) => x-2 thuộc Ư(2) <=> x-2 thuộc (+-1;+-2)
| x-2 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| x | 3(t/m) | 1(t/m) | 4(t/m) | 0(t/m) |
=> Vậy..
e) \(x^2-9=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=9\Leftrightarrow x=+-3\)thay lần lượt vào A rồi tính nha

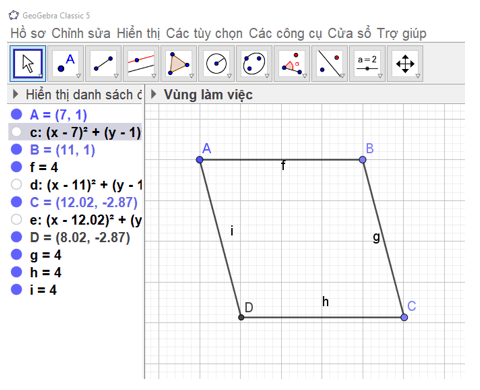
a) Dùng 

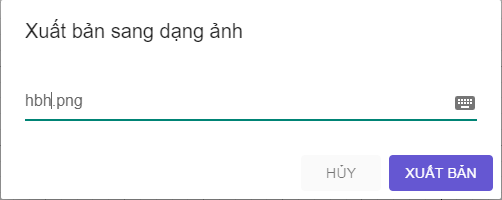
b) Lưu hình vẽ ở HĐ2 thành tệp hbh.png.
Vào Hồ sơ → Chọn Xuất bản → Chọn PNG image (.png).
Ta đổi tên tệp thành hbh (như hình vẽ), sau đó chọn xuất bản.
Bước 1. Vẽ đoạn thẳng AB và có độ dài 4 cm tương tự như Bước 1 của HĐ1.
Bước 2. Vẽ điểm C sao cho BC = 4 cm.
Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 
Bước 3. Ẩn đường tròn và thu được hình thoi ABCD.

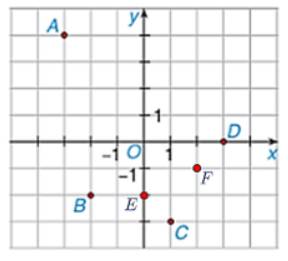
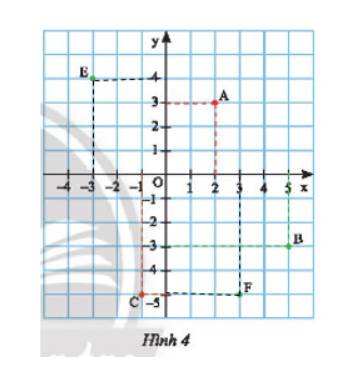
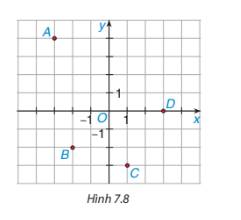
a) Có A(–3; 4), B(–2; –2), C(1; –3), D(3; 0).
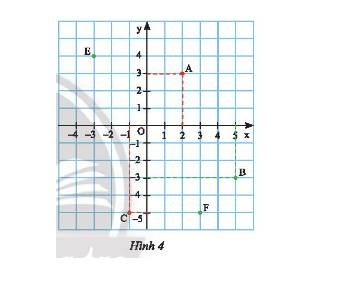
b) Ta có các điểm E(0; –2) và F(2; –1) được biểu diễn như sau:

Điểm \(O\) là gốc tọa độ nên \(O\left( {0;0} \right)\)
Từ điểm \(E\) ta vẽ vuông góc với \(Ox;Oy\) cắt \(Ox\) tại – 3 và cắt \(Oy\) tại 4 nên \(E\left( { - 3;4} \right)\).
Từ điểm \(F\) ta vẽ vuông góc với \(Ox;Oy\) cắt \(Ox\) tại 3 và cắt \(Oy\) tại – 5 nên \(E\left( {3; - 5} \right)\).

a) Dùng 
Vào Hồ sơ → Chọn Xuất bản → Chọn PNG image (.png).
Ta đổi tên tệp thành hbh (như hình vẽ), sau đó chọn xuất bản.
c) Vẽ hình thang cân ADEC có AD // EC, AD = 6 cm, CE = 4 cm, AC = DE = 3 cm theo các bước sau:
Bước 1. Vẽ đoạn thẳng AB và có độ dài bằng AD – EC = 2 cm tương tự như Bước 1 của HĐ1.
Bước 2. Vẽ tam giác ABC có BC = 3 cm (độ dài của DE), AC = 3 cm.
Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Bước 4. Vẽ điểm E sao cho DE // BC và CE // AB.
Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Chọn công cụ 

Ẩn các đường tròn, các đường thẳng, đoạn thẳng AB, BC và điểm B. Chọn công cụ 
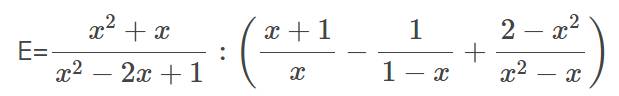



 trong công cụ
trong công cụ  để kiểm tra trung điểm AC và BD có trùng nhau không.
để kiểm tra trung điểm AC và BD có trùng nhau không.
 trong công cụ
trong công cụ  để kiểm tra DE có bằng 4 cm không.
để kiểm tra DE có bằng 4 cm không.
Đk: \(x\ne1;x\ne0\)
a) \(E=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\left[\dfrac{x+1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}.\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\)
b) \(E>1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}>1\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x-1}>0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
( do \(x^2-x+1=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall x\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
Vậy để E>1 thì x>1
c) \(E=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^2-1+1}{x-1}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+1}{x-1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}\)
\(E\in Z\Leftrightarrow x+1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}\in Z\) mà \(x\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(ktm\right);x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(x=2\) thì \(E\in Z\).