Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(a.x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
=>x=2
b) \(2x^2-x=0\)
\(x\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(x^2+y^2=0\)
Vì \(x^2,y^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
=>x=y=0
e) \(x^2+6x+10=0\)
\(\left(x+3\right)^2+1=0\)
Vì \(\left(x+3\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
=> VT>0 \(\forall x\)
=> phương trình vô nghiệm

Bài 1:
a) \(3x^2+8x-3=0\)
Hệ số: a=3,b'=4,c=(-3)
\(\Delta'=4^2-3.\left(-3\right)=25>0\)
nên pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1=\frac{-b'+\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{-4+\sqrt{25}}{3}=\frac{1}{3}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-b'-\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{-4-\sqrt{25}}{3}=-3\)
b) \(9x^2-6x+1=0\)
Hệ số: a=9,b'=3,c=1
\(\Delta'=3^2-9.1=0\left(=0\right)\)
nên pt có nghiệm kép: \(x_1=x_2=\frac{-b'}{a}=\frac{-3}{9}=\frac{-1}{3}\)
c) \(2x^2-4x+7=0\)
Hệ số: a=2,b'=(-2),c = 7
\(\Delta'=\left(-2\right)^2-2.7=-10< 0\)
nên pt vô nghiệm

a)
`4(x-2)^2 =4`
`<=>(x-2)^2 =1`
`<=>x-2=1` hoặc `x-2=-1`
`<=>x=3` hoặc `x=1`
b)
`5(x^2 -6x+9)=5`
`<=>(x-3)^2 =1`
`<=>x-3=1`hoặc `x-3=-1`
`<=>x=4` hoặc `x=2`
c)
`4x^2 +4x+1=0`
`<=>(2x+1)^2 =0`
`<=>2x+1=0`
`<=>x=-1/2`
d)
`9x^2 +6x+1=2`
`<=>(3x+1)^2 =2`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=\sqrt{2}\\3x+1=-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{2}-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: \(\text{Δ}=\left(m-5\right)^2-4\left(-m+6\right)\)
\(=m^2-10m+25+4m-24\)
\(=m^2-6m+1=\left(m-3\right)^2-8\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì \(\left(m-3\right)^2>=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>=2\sqrt{2}+3\\m< =-2\sqrt{2}+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x_1+3x_2=13\\x_1+x_2=m-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x_1+3x_2=13\\2x_1+2x_2=2m-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=13-2m+10=-2m+25\\x_1=m-5+2m-25=3m-30\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1x_2=-m+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-25\right)\left(3m-30\right)=m-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6m^2-60m-75m+750-m+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6m^2-136m+756=0\)
hay \(m\in\left\{\dfrac{34+\sqrt{22}}{3};\dfrac{34-\sqrt{22}}{3}\right\}\)
b: \(x_1+x_2+x_1x_2-11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m-5-m+6-11=0\)
=>-12=0(vô lý)

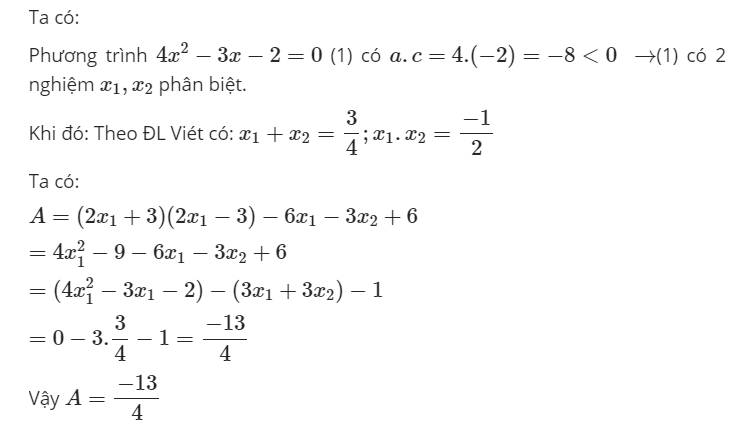
\(a,x^2+4x=-3\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+3=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,3x^2+4x-4=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x-2x-4=0\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)-2\left(x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=\frac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2+5x-6=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,x^2-6x=-9\Leftrightarrow x^2+6x+9=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
cảm ơn thần đồng toán hc nhen