Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 1:
a, Ta có:
\(\dfrac{x.\dfrac{xy}{x-y}}{x+\dfrac{xy}{x-y}}-\dfrac{y.\dfrac{xy}{x-y}}{y-\dfrac{xy}{x-y}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2y}{x-y}}{x+\dfrac{xy}{x-y}}-\dfrac{\dfrac{xy^2}{x-y}}{y-\dfrac{xy}{x-y}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{x^2y}{x-y}\right)\left(y-\dfrac{xy}{x-y}\right)-\left(\dfrac{xy^2}{x-y}\right)\left(x+\dfrac{xy}{x-y}\right)}{\left(x+\dfrac{xy}{x-y}\right)\left(y-\dfrac{xy}{x-y}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2y^2}{x-y}-\dfrac{x^3y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}-\dfrac{x^2y^2}{x-y}-\dfrac{x^2y^3}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}{xy-\dfrac{x^2y}{x-y}+\dfrac{xy^2}{x-y}-\dfrac{x^2y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\left(\dfrac{x^3y^2+x^2y^3}{\left(x-y\right)^2}\right)}{xy-\left(\dfrac{x^2y-xy^2}{x-y}\right)-\dfrac{x^2y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}\)
\(=-\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2y^2\left(x+y\right)}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}{xy-\left(\dfrac{xy\left(x-y\right)}{\left(x-y\right)}\right)-\dfrac{x^2y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2y^2\left(x+y\right)}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}{\dfrac{x^2y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}}=x+y\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!! Làm một câu mà toát cả mồ hôi!

a, Ta có : \(A=\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{2x}{4-x^2}+\frac{3}{x-2}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{2x}{\left(2-x\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{3}{x-2}\)
\(=\frac{x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{2x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{3\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x-2+2x+3x+6}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{6x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
Suy ra : \(M=\frac{6x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}.\frac{x+2}{3x+2}\)
\(=\frac{2\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+2\right)}=\frac{2}{x-2}\)

a, ĐKXĐ : \(x-1\ne0\)
=> \(x\ne1\)
TH1 : \(x-2\ge0\left(x\ge2\right)\)
=> \(\left|x-2\right|=x-2=1\)
=> \(x=3\left(TM\right)\)
- Thay x = 3 vào biểu thức P ta được :
\(P=\frac{3+2}{3-1}=\frac{5}{2}\)
TH2 : \(x-2< 0\left(x< 2\right)\)
=> \(\left|x-2\right|=2-x=1\)
=> \(x=1\left(KTM\right)\)
Vậy giá trị của P là \(\frac{5}{2}\) .
a) \(P=\frac{x+2}{x-1}\) \(\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne1\right)\)
Ta có: \(\left|x-2\right|=1\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=1\\x-2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (loại x = 1 vì x ≠ 1)
Thay \(x=3\) vào P, ta có:
\(P=\frac{3+2}{3-2}=\frac{5}{1}=5\)
Vậy P = 5 tại x = 3.
b) \(Q=\frac{x-1}{x}+\frac{2x+1}{x^2+x}=\frac{x-1}{x}+\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x^2-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) (ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ -1)
\(=\frac{x^2+2x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x+2}{x+1}\)

Để \(Q\) nhỏ nhất => \(m;n\) nhỏ nhất
=>\(m^2+n^2\) nhỏ nhất
Mà \(m^2;n^2\ge0\)
Suy ra để \(Q\) nhỏ nhất thì

a: Khi x=1 thì \(A=\dfrac{1+1}{2}=1\)
b: Để A=2 thì x+1=4
=>x=3
c: \(B=\dfrac{2+x-2+x}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
d: C=A*B=2/(x-2)*x+1/2=x+1/x-2
Để C la số nguyên thì x-2+3 chia hết cho x-2
=>\(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;5;-1;1\right\}\)

a, \(I=s\left(s^2-t\right)+\left(t^2+s\right)=s^3-st+t^2+s\)
Thay t = -1 và s = 1 vào biểu thức trên ta được :
\(1+1+1+1=4\)
b, \(N=u^2\left(u-v\right)-v\left(v^2-u^2\right)=u^2\left(u-v\right)+v\left(u+v\right)\left(u-v\right)\)
\(=\left(u-v\right)\left(u^2+v\left(u+v\right)\right)\)
Thay \(u=0,5=\frac{1}{2};v=-\frac{1}{2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\right).\frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{4}\)

Bài 1:
a) x≠2x≠2
Bài 2:
a) x≠0;x≠5x≠0;x≠5
b) x2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5xx2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5x
c) Để phân thức có giá trị nguyên thì x−5xx−5x phải có giá trị nguyên.
=> x=−5x=−5
Bài 3:
a) (x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45
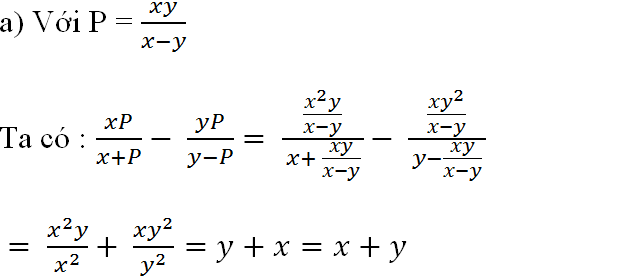
a) Thay phân thức P vào biểu thức A rồi rút gọn chúng ta thu được A = u + v với điều kiện các biểu thức có nghĩa.
b) Tương tự a) ta có B = 1.