
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Cách 1:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 22. (x -1)2 = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 – [ 2(x – 1)]2 =0
⇔ [(x+ 1) + 2( x- 1)]. [(x+ 1) - 2( x- 1)]= 0
⇔ ( x+1+ 2x -2) . (x+1 – 2x + 2) =0
⇔ ( 3x- 1).( 3- x) = 0
⇔ 3x – 1 = 0 hoặc 3 – x= 0
+) 3x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 1 ⇔ x = 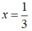
+) 3 – x = 0 ⇔ x= 3
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
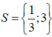
* Cách 2: Ta có:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ x2 + 2x +1- 4x2 + 8x – 4 = 0
⇔ - 3x2 + 10x – 3 = 0
⇔ (- 3x2 + 9x) + (x – 3) = 0
⇔ -3x (x – 3)+ ( x- 3) = 0
⇔ ( x- 3). ( - 3x + 1) = 0
⇔ x - 3 = 0 hoặc -3x + 1= 0
+) x - 3 = 0 x = 3
+) - 3x + 1 = 0 - 3x = - 1 ⇔ x = 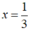
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
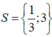
\(\left(x+1\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(< =>\left(x+1\right)^2=\left(2x-2\right)^2\)
\(< =>\left(x+1-2x+2\right)\left(x+1+2x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}-x+3=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)

3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)

\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

a) \(9x^2-1=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)-\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{-1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
b) \(\left(4x-3\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2-24x+9=4x^2-8x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-16x+5=0\)
Ta có \(\Delta=16^2-4.12.5=16,\sqrt{\Delta}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{16+4}{12}=\frac{5}{3}\\x=\frac{16-4}{12}=1\end{cases}}\)

2 x 2 + 5x + 3 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 2x + 3x + 3 = 0
⇔ 2x(x + 1) + 3(x + 1) = 0 ⇔ (2x + 3)(x + 1) = 0
⇔ 2x + 3 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
2x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -1,5
x + 1 = 0 ⇔ x = -1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -1,5 hoặc x = -1

(2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
⇔ (2x + 1)(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)(2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).[(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).(3x – 2 – 5x + 8) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(6 – 2x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1 = 0 hoặc 6 – 2x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 6 – 2x = 0 ⇔ 6 = 2x ⇔ x = 3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 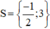

x 2 – 5 = (2x - 5 )(x + 5 )
⇔ (x + 5 )(x - 5 ) = (2x - 5 )(x + 5 )
⇔ (x + 5 )(x - 5 ) – (2x - 5 )(x + 5 ) = 0
⇔ (x + 5 )[(x - 5 ) – (2x - 5 )] = 0
⇔ (x + 5 )(- x) = 0 ⇔ x + 5 = 0 hoặc – x = 0
x + 5 = 0 ⇔ x = - 5
x = 0 ⇔ x = 0
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = - 5 hoặc x = 0.

bạn đăng tách cho mn cùng giúp nhé
Bài 1 :
a, \(\Leftrightarrow11-x=12-8x\Leftrightarrow7x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x^2+4x+4\right)-8x^2=2\left(x^3-8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+8x^2+8x-8x^2=2x^3-16\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow3-2x=-x-4\Leftrightarrow x=7\)
d, \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8+9x^2-1=x^3+3x^2+3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+12x-9=3x^2+3x+1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{10}{9}\)
e, \(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x-3=2x^2+9x-5\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
f, \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3-2x^2-x=10x-5x^2-11x-22\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x^2+2x-1=-5x^2-x-22\Leftrightarrow3x=-21\Leftrightarrow x=-7\)

4 x 2 – 12x + 5 = 0 ⇔ 4 x 2 – 2x – 10x + 5 = 0
⇔ 2x(2x – 1) – 5(2x – 1) = 0 ⇔ (2x – 1)(2x – 5) = 0
⇔ 2x – 1 = 0 hoặc 2x – 5 = 0
2x – 1 = 0 ⇔ x = 0,5
2x – 5 = 0 ⇔ x = 2,5
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 0,5 hoặc x = 2,5
\(\left(4x+3\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+3\right)^2=4\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+3\right)^2-4\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+3+2x-2\right)\left(4x+3-2x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+1\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{1}{6}\\x=-\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
\(\left(4x+3\right)^2=4x^2-8x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+3\right)^2=\left(2x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(6x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-5=0\\6x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=\frac{-1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)