
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: \(=\dfrac{-5}{7}\left(\dfrac{2}{11}+\dfrac{9}{11}\right)+\dfrac{13}{4}=\dfrac{-5}{7}+\dfrac{13}{4}=\dfrac{-20+91}{28}=\dfrac{71}{28}\)
c: \(=\dfrac{146}{13}-3-\dfrac{68}{13}=6-3=3\)
d: \(=\dfrac{2}{7}\left(\dfrac{21}{4}-\dfrac{13}{4}\right)=\dfrac{4}{7}\)

1: \(=75\left(27+25-2\right)=75\cdot50=3750\)
2: \(=15\left(23+37\right)+55=15\cdot60+55=955\)
3: \(=36\cdot14+36\cdot17+36\cdot69\)
\(=36\cdot100=3600\)
4: \(=200\cdot\left(32+68\right)=200\cdot100=20000\)

Ta thấy:
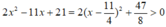
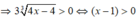
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cô – si ta có:
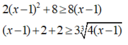
Cộng vế với vế ta được:
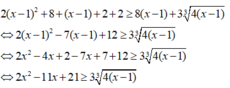
Dấu “=” xảy ra khi và chỉ khi x - 1 = 2 ⇔ x = 3
Vậy x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình.

a,\(\left|9+x\right|=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}9+x=2x\\9x+x=-2x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}9=x\\9=-3x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=9\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
Trường hợp 2 chưa chắc chắn lắm!!!
a) \(\left|9+x\right|=2x\)
Xét trường hợp 1:
\(9+x=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9+x-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=9\)
Xét trường hợp 2:
\(9+x=-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9+x-\left(-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9+x+2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-9:3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
Vậy x=9 hoặc x=-3
b) \(\left|x+6\right|-9=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x+6\right|=2x+9\)
Xét trường hợp 1:
\(x+6=2x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+6-\left(2x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+6-2x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
Xét trường hợp 2:
\(x+6=-\left(2x+9\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+6-\left[-\left(2x+9\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+6+\left(2x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+6+2x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-15:3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy x=-3 hoặc x=-5

ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge16\\y\ge9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ pt thứ nhất của hệ:
\(\frac{8xy}{x^2+y^2+6xy}+\frac{17}{8}\left(\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}\right)=\frac{21}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{8}{\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}+6}+\frac{17}{8}\left(\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}\right)=\frac{21}{4}\)
Đặt \(\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}=t\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{8}{6+t}+\frac{17}{8}t=\frac{21}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{17}{8}t^2+\frac{15}{2}t-\frac{47}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\\t=-\frac{94}{17}< 0\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}=2\Leftrightarrow x^2+y^2=2xy\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=y\)
Thay xuống pt dưới:
\(\sqrt{x-16}+\sqrt{x-9}=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-16}-3+\sqrt{x-9}-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-25}{\sqrt{x-16}+3}+\frac{x-25}{\sqrt{x-9}+4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-\dfrac{9}{2}\\x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(3+\sqrt{9+2x}\right)^2.2x^2}{\left(3-\sqrt{9+2x}\right)^2\left(3+\sqrt{9+2x}\right)^2}< x+21\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(3+\sqrt{9+2x}\right)^2.2x^2}{4x^2}< x+21\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3+\sqrt{9+2x}\right)^2< 2x+42\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+9+3\sqrt{9+2x}< x+21\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{9+2x}< 4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9+2x< 16\Rightarrow x< \dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{9}{2}\le x< \dfrac{7}{2}\\x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)

Chắc dưới mẫu bạn ghi nhầm căn đầu tiên
ĐKXĐ: \(-21\le x\le21;x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(\sqrt{21+x}+\sqrt{21-x}\right)^2}{21+x-21+x}=\frac{21}{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{42+2\sqrt{21^2-x^2}}{2x}=\frac{21}{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{21^2-x^2}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\pm21\)

\(43+\left(9-21\right)=317-\left(x+317\right)\)
\(43+9-21=317-x-317\)
\(31=317-317-x\)
\(31=0-x\)
\(\Rightarrow x+0=-31\)
\(x=\left(-31\right)-0\)
\(x=-31\)
\(43+\left(9-21\right)=317-\left(x+317\right)\)
\(43+\left(-12\right)=317+x-317\)
\(31=317+x+\left(-317\right)\)
\(31=317+\left(-317\right)+x\)
\(31=0+x\)
\(31=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=31\)
Vậy \(x=31\) là giá trị cần tìm