Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của d₁ và d₂
x + 2 = 5 - 2x
⇔ x + 2x = 5 - 2
⇔ 3x = 3
⇔ x = 1
Thay x = 1 vào d₁ ta có:
y = 1 + 2 = 3
⇒ Giao điểm của d₁ và d₂ là A(1; 3)
Thay tọa độ điểm A vào d₃ ta có:
VT = 3
VP = 3.1 = 3
⇒ VT = VP
Hay A ∈ d₃
Vậy d₁, d₂ và d₃ đồng quy
b) Thay tọa độ điểm A(1; 3) vào d₄ ta có:
m.1 + m - 5 = 3
⇔ 2m - 5 = 3
⇔ 2m = 3 + 5
⇔ 2m = 8
⇔ m = 8 : 2
⇔ m = 4
Vậy m = 4 thì d₁, d₂ và d₄ đồng quy

a, d1//d2 <=> 2m-1= m+1 <=> 2m-m = 1+1 <=> m=2
a: Để (d1)//(d2) thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m-1=m+1\\-2m+5< >m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m-m=1+1\\-2m-m< >-1-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\-3m\ne-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
b: Để (d1) cắt (d2) thì \(2m-1\ne m+1\)
=>\(2m-m\ne1+1\)
=>\(m\ne2\)

a: Để (d)//(d1) thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\-5< >3\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m+1=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(m=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b: Thay x=2 vào y=x+3, ta được:
\(y=2+3=5\)
Thay x=2 và y=5 vào (d), ta được:
\(2\left(m+1\right)-5=5\)
=>2(m+1)=10
=>m+1=5
=>m=5-1=4
c: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\left(m+1\right)x-5=0\cdot\left(m+1\right)-5=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>A(0;-5)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(-5-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{0^2+5^2}=5\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m+1\right)x-5=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m+1\right)x=5\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{m+1}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(B\left(\dfrac{5}{m+1};0\right)\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{5}{m+1}-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{5}{m+1}\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{\left|m+1\right|}\)
Ox\(\perp\)Oy
=>OA\(\perp\)OB
=>ΔOAB vuông tại O
ΔOAB vuông tại O
=>\(S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot5\cdot\dfrac{5}{\left|m+1\right|}=\dfrac{25}{2\left|m+1\right|}\)
Để \(S_{AOB}=5\) thì \(\dfrac{25}{2\left|m+1\right|}=5\)
=>\(2\left|m+1\right|=5\)
=>|m+1|=5/2
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+1=\dfrac{5}{2}\\m+1=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{3}{2}\\m=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a:
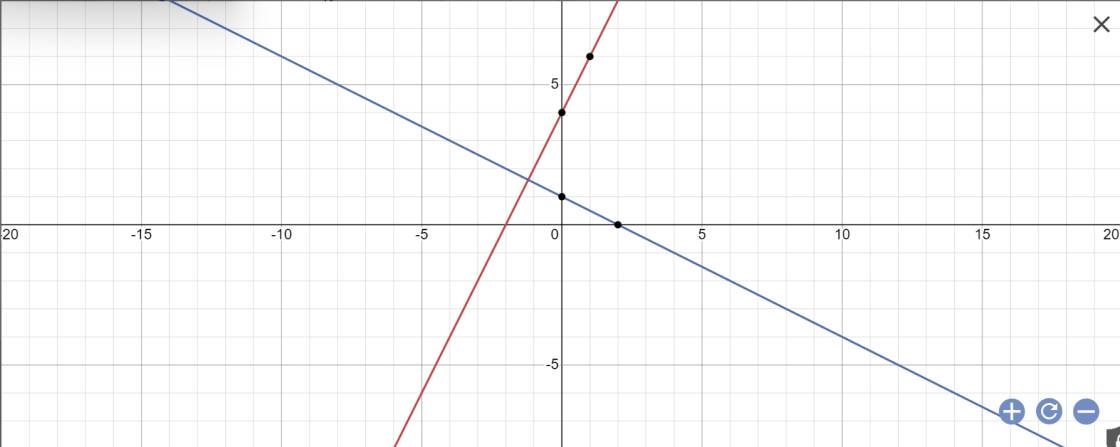
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2x+4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0+4=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-\dfrac{1}{2}x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ M là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\\y=2x+4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{2}x=-3\\y=2x+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-3:\dfrac{5}{2}=-3\cdot\dfrac{2}{5}=-\dfrac{6}{5}\\y=2\cdot\dfrac{-6}{5}+4=\dfrac{-12}{5}+4=\dfrac{8}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
A(-2;0); C(2;0); M(-1,2;1,6)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(2+2\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{4^2}=4\)
\(AM=\sqrt{\left(-1,2+2\right)^2+\left(1,6-0\right)^2}=\dfrac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
\(CM=\sqrt{\left(-1,2-2\right)^2+1,6^2}=\dfrac{8\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
Vì \(MA^2+MC^2=AC^2\)
nên ΔMAC vuông tại M
c: Vì ΔMAC vuông tại M
nên \(S_{MAC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot MA\cdot MC=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}\cdot\dfrac{8\sqrt{5}}{5}=\dfrac{2\cdot8}{5}=\dfrac{16}{5}\)

ai giup vs
Cho x,y là hai số thoả mãn 2(x2+y2)=(x-y)2 Khi đó ta có hệ thức biểu diễn mối quan hệ giữa x,y là x=....y
giải chi tiết nha
Lời giải:
Để $(d_2)\parallel (d_1)$ thì:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} -7=2m+5\\ 2\neq -3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow -7=2m+5\Leftrightarrow m=-6\)