
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Áp dụng định lý Py-ta-go cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A ta có:
\(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=\sqrt{3^2+4^2}=5\left(cm\right)\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{3}{15}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{AC}{DF}=\dfrac{4}{20}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{5}{25}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{AC}{DF}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
Xét hai tam giác ABC và DEF có:
\(\dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{AC}{DF}=\dfrac{BC}{EF}\left(=\dfrac{1}{5}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\sim\Delta DEF\left(c.c.c\right)\)

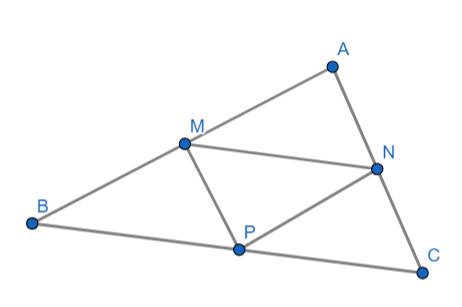
a) Ta có:
M là trung điểm của AB
N là trung điểm của AC
⇒ MN là đường trung bình của tam giác ABC
⇒ MN // BC
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{AMN}=\widehat{ABC}\) (đồng vị)
Xét hai tam giác ABC và AMN có:
\(\widehat{AMN}=\widehat{ABC}\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\widehat{BAC}\) chung
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\sim\Delta AMN\left(g.g\right)\)
b) Chứng minh tương tự như câu a thì ta có:
PN cũng là đường trung bình của tam giác ABC \(\Rightarrow PN=\dfrac{1}{2}AB\)
PM cũng là đường trung bình của tam giác ABC \(\Rightarrow PM=\dfrac{1}{2}AC\)
Mà: \(NM=\dfrac{1}{2}BC\) (NM là đường trung bình ...)
Xét hai tam giác ABC và PNM có:
\(\dfrac{PN}{AB}=\dfrac{PM}{AC}=\dfrac{NM}{BC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\sim\Delta PNM\left(c.c.c\right)\)

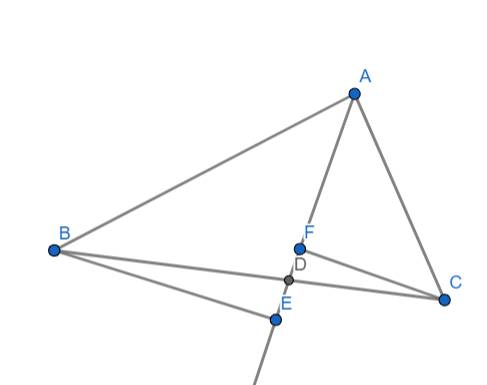
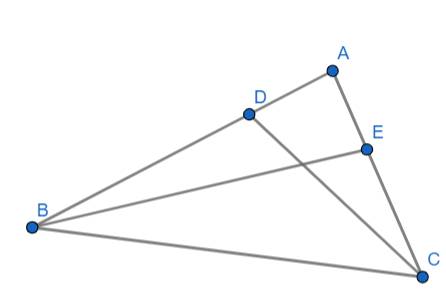
a) Ta có: E,F lần lược là hình chiếu của B,C trên AD
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{BEA}=90^o\\\widehat{CFA}=90^o\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét hai tam giác ABE và ACF có:
\(\widehat{BEA}=\widehat{CFA}\left(=90^o\right)\)
\(\widehat{BAE}=\widehat{CAF}\) (do AD là phân giác của góc A)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABE\sim\Delta ACF\left(g.g\right)\)
b) Xét hai tam giác BDE và CDF có:
\(\widehat{BDE}=\widehat{CDF}\) (đối đỉnh)
\(\widehat{BED}=\widehat{CFD}\left(=90^o\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta BDE\sim\Delta CDF\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{BE}{CF}=\dfrac{DE}{DF}\) (1)
Mà: \(\Delta ABE\sim\Delta ACF\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{BE}{CF}=\dfrac{AE}{AF}\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) ta có: \(\dfrac{DE}{DF}=\dfrac{AE}{AF}\Rightarrow AF\cdot DE=AE\cdot DF\)

a) Đường thẳng \(y=ax+b\) song song với đường thẳng \(y=4x-3\)
Nên có \(a=4\) đường thẳng có dạng \(y=3x+b\left(b\ne-3\right)\)
Mà \(y=3x+b\) đi qua điểm \(I\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{3}{4}\right)\) nên ta thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2};y=\dfrac{3}{4}\) ta có:
\(\dfrac{3}{4}=3\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{3}{2}+b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b=\dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b=-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: \(y=4x-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
b) Đường thẳng \(y=ax+b\) có hệ số góc \(a=3\) nên có dạng \(y=3x+b\)
Do đường thẳng cắt trục tung tại điểm có tung độ là - 4 nên ta thay \(x=0;y=-4\)
\(-4=0\cdot3+b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b=-4\)
Vậy: \(y=3x-4\)

\(y=\left(m-3\right)+m^2\) có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=m-3\\b=m^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) Để \(y=\left(m-3\right)x+m^2\) cắt \(y=3x+5\) thì:
\(a\ne a'\) hay:
\(m-3\ne3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ne3+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ne6\)
b) Để \(y=\left(m-3\right)x+m^2\) song song với \(y=-2x+1\) thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=a'\\b\ne b'\end{matrix}\right.\) hay:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3=-2\\m^2\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=-2+3\\m\ne\pm1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m\ne\pm1\end{matrix}\right.\) (ktm)
Vậy không có m thỏa mãn
c) Để \(y=\left(m-3\right)x+m^2\) trùng với \(y=-x+4\) thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=a'\\b=b'\end{matrix}\right.\) hay:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3=-1\\m^2=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=-1+3\\m=\pm2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m=\pm2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=2\)

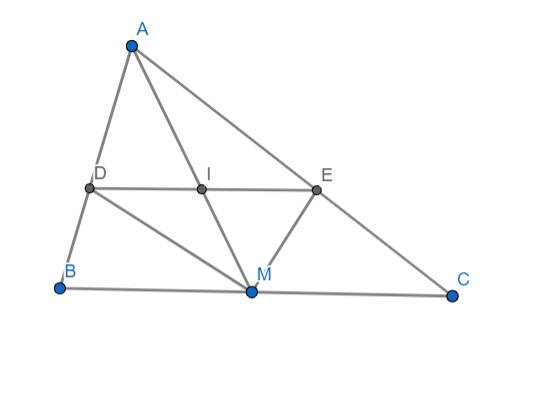
a) Ta có ME là tia phân giác của góc AMC nên:
\(\dfrac{AM}{AE}=\dfrac{MC}{CE}\Rightarrow\dfrac{AM}{MC}=\dfrac{AE}{CE}\) (1)
MD là tia phân giác của góc AMB nên:
\(\dfrac{AM}{AD}=\dfrac{BM}{BD}\Rightarrow\dfrac{AM}{BM}=\dfrac{AM}{CM}=\dfrac{AD}{BD}\) (vì M là trung điểm của BC nên BM = CM) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) ta có: \(\dfrac{AE}{CE}=\dfrac{AD}{BD}\Rightarrow DE//BC\)
b) Ta có: \(\Delta ADE\sim\Delta ABC\left(g.g\right)\) (vì có DE//BC)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{DE}{BC}=\dfrac{AE}{AC}\) (3)
\(\Delta AIE\sim\Delta AMC\left(g.g\right)\) (vì có IE//MC)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{IE}{MC}=\dfrac{AE}{AC}\) (4)
Từ (3) và (4) ta có: \(\dfrac{DE}{BC}=\dfrac{IE}{MC}\Rightarrow\dfrac{DE}{IE}=\dfrac{BC}{MC}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow DE=2IE\)
Hay I là trung điểm của DE


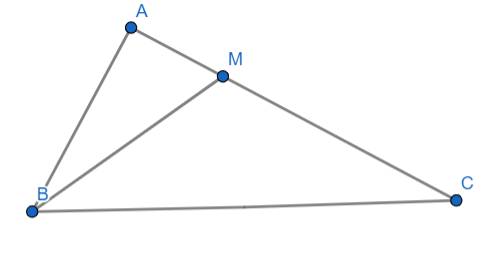
a) Áp dụng định lý Py-ta-go cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A ta có:
\(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=\sqrt{10^2+20^2}=10\sqrt{5}\left(cm\right)\)
Áp dụng định lý Py-ta-go cho tam giác ABM vuông tại A ta có:
\(BM^2=AB^2+AM^2\)
\(\Rightarrow BM=\sqrt{AB^2+AM^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow BM=\sqrt{10^2+5^2}=5\sqrt{5}\left(cm\right)\)
b) Ta có:
\(\dfrac{AM}{AB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{BM}{BC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{AM}{AB}=\dfrac{MB}{BC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Xét hai tam giác ABC và AMB có:
\(\widehat{BAC}\) chung
\(\dfrac{AM}{AB}=\dfrac{MB}{BC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\sim\Delta AMB\left(c.g.c\right)\)

a) Xét hai tam giác ABE và ACD có:
\(\widehat{ACD}=\widehat{ABE}\left(gt\right)\)
\(\widehat{BAC}\) chung
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABE\sim\Delta ACD\left(g.g\right)\)
b) Ta có: \(\Delta ABE\sim\Delta ACD\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{AE}{AD}\)

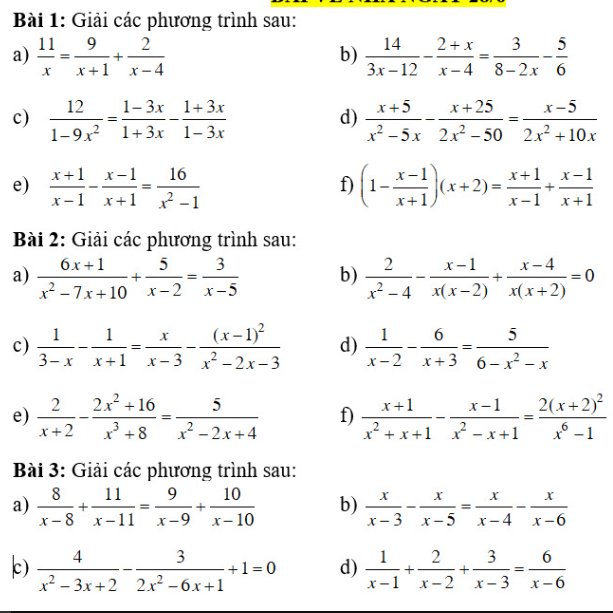
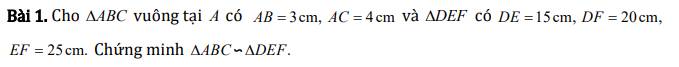

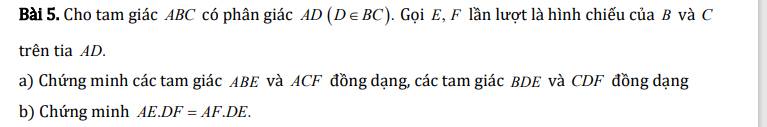
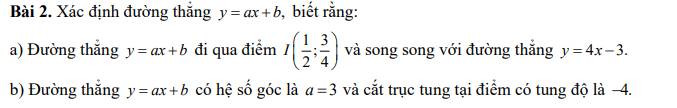


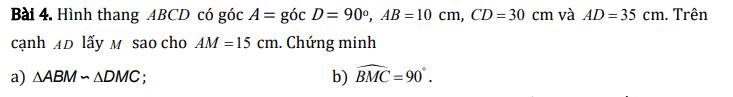
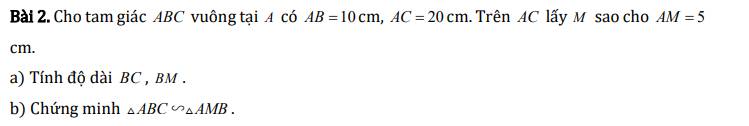
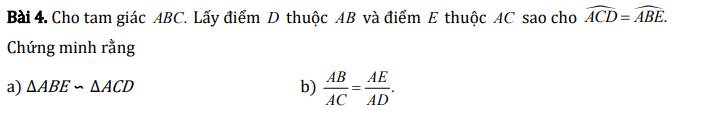

Bài 1:
e: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{16}{x^2-1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{16}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=16\)
=>\(\left(x+1+x-1\right)\left(x+1-x+1\right)=16\)
=>4x=16
=>x=4(nhận)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1-1\right\}\)
\(\left(1-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\right)\left(x+2\right)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}+\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+1-x+1}{\left(x+1\right)}\left(x+2\right)=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=2\left(x^2+1\right)\)
=>\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=x^2+1\)
=>\(x^2+x-2=x^2+1\)
=>x-2=1
=>x=3(nhận)
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-1;4\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{11}{x}=\dfrac{9}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x-4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{11}{x}=\dfrac{9\left(x-4\right)+2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{11}{x}=\dfrac{11x-34}{x^2-3x-4}\)
=>\(11\left(x^2-3x-4\right)=x\left(11x-34\right)\)
=>\(11x^2-33x-44=11x^2-34x\)
=>-33x-44=-34x
=>-33x+34x=44
=>x=44(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne4\)
\(\dfrac{14}{3x-12}-\dfrac{2+x}{x-4}=\dfrac{3}{8-2x}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-4}=\dfrac{-3}{2\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{28}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x+2\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{-9}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5\left(x-4\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}\)
=>28-6(x+2)=-9-5(x-4)
=>28-6x-12=-9-5x+20
=>-6x+16=-5x+11
=>-6x+5x=11-16
=>-x=-5
=>x=5(nhận)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};-\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{12}{1-9x^2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{1+3x}-\dfrac{1+3x}{1-3x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{12}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}=\dfrac{\left(1-3x\right)^2-\left(1+3x\right)^2}{\left(1+3x\right)\left(1-3x\right)}\)
=>\(\left(1-3x\right)^2-\left(1+3x\right)^2=12\)
=>\(9x^2-6x+1-9x^2-6x-1=12\)
=>-12x=12
=>x=-1(nhận)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;5;-5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+5}{x^2-5x}-\dfrac{x+25}{2x^2-50}=\dfrac{x-5}{2x^2+10x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5}{x\left(x-5\right)}-\dfrac{x+25}{2\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-5}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x+5\right)^2}{2x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x+25\right)}{2x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
=>\(2\left(x+5\right)^2-x\left(x+25\right)=\left(x-5\right)^2\)
=>\(2x^2+20x+50-x^2-25x=x^2-10x+25\)
=>-5x+50=-10x+25
=>5x=-25
=>x=-5(loại)
Bài 2:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}+\dfrac{5\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
=>6x+1+5x-25=3x-6
=>11x-24=3x-6
=>8x=18
=>x=9/4(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x-4}{x\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
=>2x-(x-1)(x+2)+(x-4)(x-2)=0
=>\(2x-\left(x^2+x-2\right)+x^2-6x+8=0\)
=>\(x^2-4x+8-x^2-x+2=0\)
=>-5x+10=0
=>x=2(loại)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-1}{x-3}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{x}{x-3}+\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(-1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)-x+3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>-(x+1)^2-x+3+(x-1)2=0
=>\(-x^2-2x-1-x+3+x^2-2x+1=0\)
=>-5x+3=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{3}{5}\left(nhận\right)\)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-3\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{6}{x+3}=\dfrac{5}{6-x^2-x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+3-6\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{-5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>x+3-6(x-2)=-5
=>x+3-6x+12+5=0
=>-5x+20=0
=>x=4(nhận)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>-2
\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{x^3+8}=\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-2x^2-16-5x-10}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=0\)
=>\(2x^2-4x+8-2x^2-5x-26=0\)
=>-9x-18=0
=>x=-2(loại)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x^2+x+1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-x+1}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^6-1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
=>2(x^2-1)=2(x+2)^2
=>\(x^2-1=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+4x+4-x^2+1=0\)
=>4x+5=0
=>\(x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\left(nhận\right)\)
Bài 3:
c:
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-1}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{3x-12}{x-6}\)
=>
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;2;\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt{7}}{2}\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{4}{x^2-3x+2}-\dfrac{3}{2x^2-6x+1}+1=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{4\left(2x^2-6x+1\right)-3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)}{\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(2x^2-6x+1\right)}=-1\)
=>\(8x^2-24x+4-3x^2+9x-6=-\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left[2\cdot\left(x^2-3x\right)+1\right]\)
=>\(5x^2-15x-2=-\left[2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+2\right]\)
=>\(5\left(x^2-3x\right)-2+2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+2=0\)
=>\(2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+10\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-3x\right)\left(x^2-3x+5\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-3x+5=\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{11}{4}>=\dfrac{11}{4}>0\forall x\)
nên x(x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
a:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{8;9;10;11\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{8}{x-8}+\dfrac{11}{x-11}=\dfrac{9}{x-9}+\dfrac{10}{x-10}\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{8}{x-8}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{11}{x-11}+1\right)=\left(\dfrac{9}{x-9}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{10}{x-10}+1\right)\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-8}+\dfrac{x}{x-11}-\dfrac{x}{x-9}-\dfrac{x}{x-10}=0\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{1}{x-8}+\dfrac{1}{x-11}-\dfrac{1}{x-9}-\dfrac{1}{x-10}\right)=0\)
=>x=0(nhận)
b:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;4;5;6\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{x}{x-5}=\dfrac{x}{x-4}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x-6\right)-x\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-2x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{-2x}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}-\dfrac{1}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\right)=0\)
=>\(x\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}=0\)
=>\(x\left(x^2-10x+24-x^2+8x-15\right)=0\)
=>x(-2x+9)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{9}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)