
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




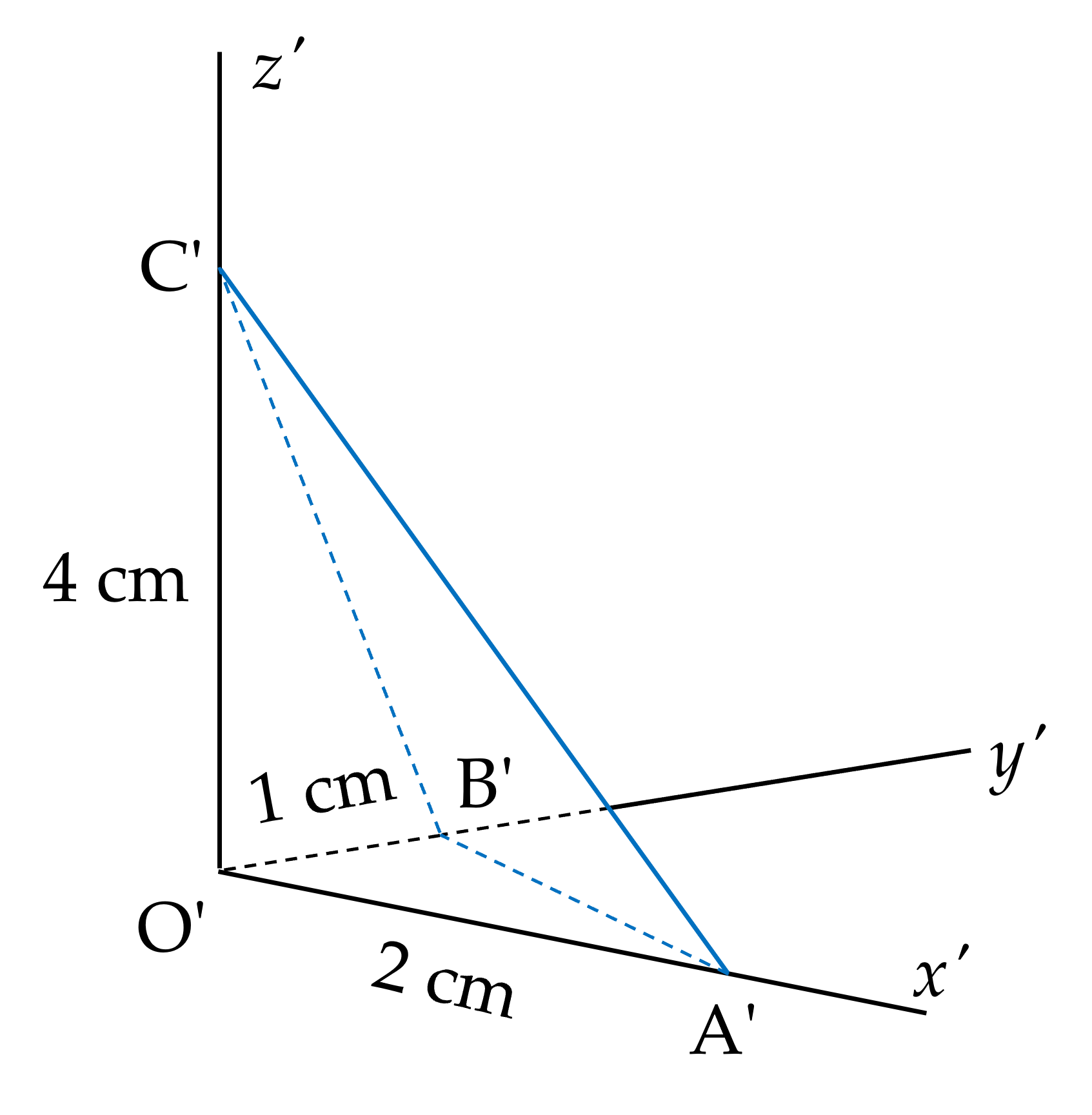
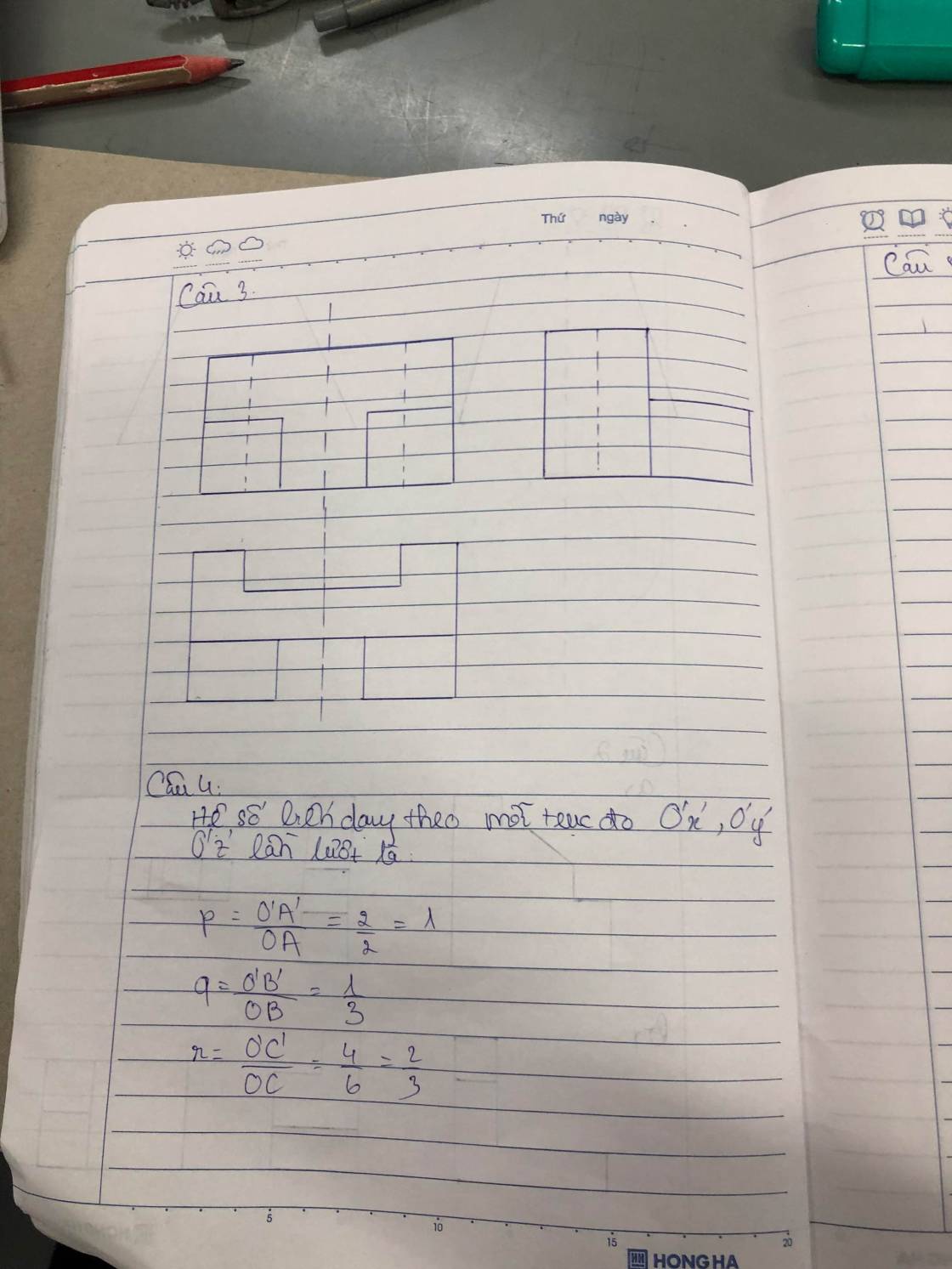
Hệ số biến dạng theo mỗi trục đo O'x', O'y', O'z' lần lượt là:
p=O'A'OA=22=1�=�'�'��=22=1;
q=O'B'OB=13�=�'�'��=13;
r=O'C'OC=46=23�=�'�'��=46=23.

a)

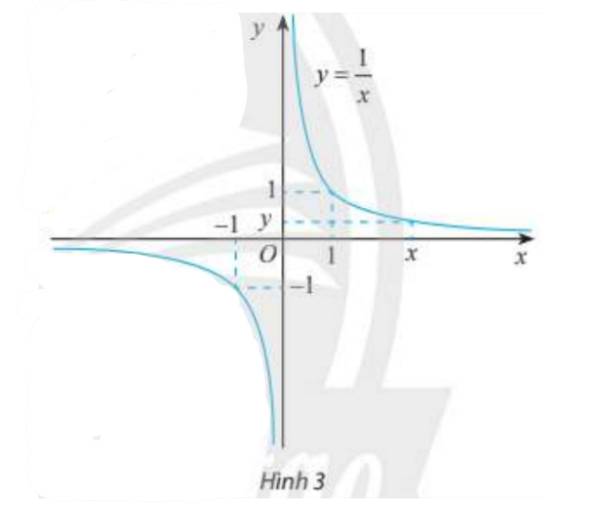
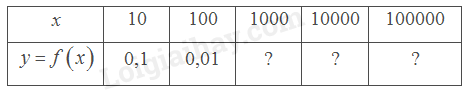
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng lớn (dần tới \( + \infty \)).
b)
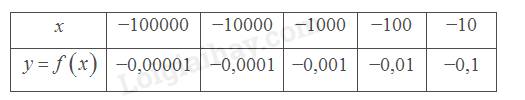
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng bé (dần tới \( - \infty \)).


1.
\(u_{n+1}=4u_n+3.4^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_{n+1}-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(n+1\right).4^{n+1}=4\left[u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n\right]\)
Đặt \(u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n=v_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}v_1=2-\dfrac{3}{4}.4=-1\\v_{n+1}=4v_n\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow v_n=-1.4^{n-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow u_n=\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n-4^{n-1}=\left(3n-1\right)4^{n-1}\)
2.
\(a_n=\dfrac{a_{n-1}}{2n.a_{n-1}+1}\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=2n+\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}-\left(n-1\right)^2-\left(n-1\right)\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=b_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b_1=2-1-1=0\\b_n=b_{n-1}=...=b_1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=n^2+n\Rightarrow a_n=\dfrac{1}{n^2+n}\)

ĐKXĐ: \(-2\le x\le3\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x+2}+2\sqrt{3-x}=a\Rightarrow4\sqrt{6+x-x^2}-3x=a^2-14\)
Mặt khác \(a^2=\left(\sqrt{x+2}+2\sqrt{3-x}\right)^2\le5\left(x+2+3-x\right)=25\)
\(\Rightarrow a\le5\)
Và \(\sqrt{x+2}+\sqrt{3-x}+\sqrt{3-x}\ge\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{3-x}\ge\sqrt{5}\) \(\Rightarrow a\ge\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{5}\le a\le5\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(a^2-14=ma\Leftrightarrow\frac{a^2-14}{a}=m\) với \(a\in\left[\sqrt{5};5\right]\)
\(f\left(a\right)=\frac{a^2-14}{a}\Rightarrow f'\left(a\right)=\frac{2a^2-a^2+14}{a^2}=\frac{a^2+14}{a^2}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)\) đồng biến \(\Rightarrow f\left(\sqrt{5}\right)\le f\left(a\right)\le5\)
\(\Rightarrow-\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}\le f\left(a\right)\le\frac{11}{5}\Rightarrow-\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}\le m\le\frac{11}{5}\)


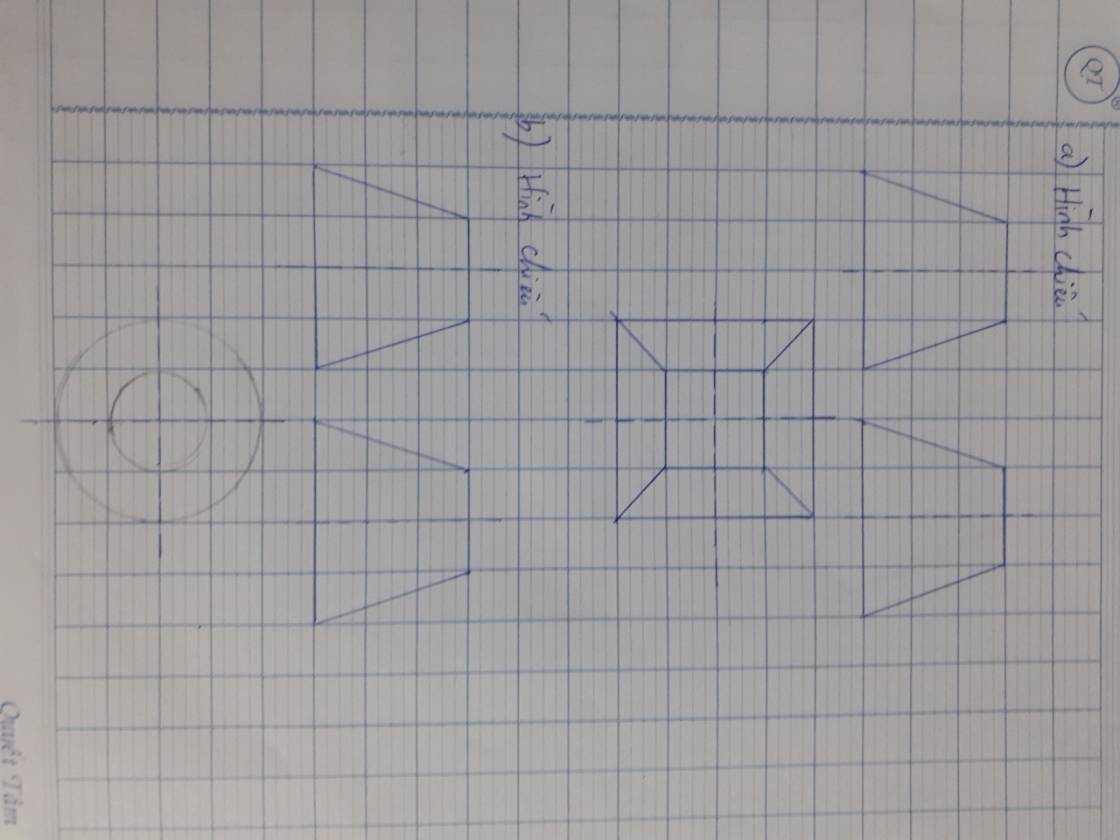
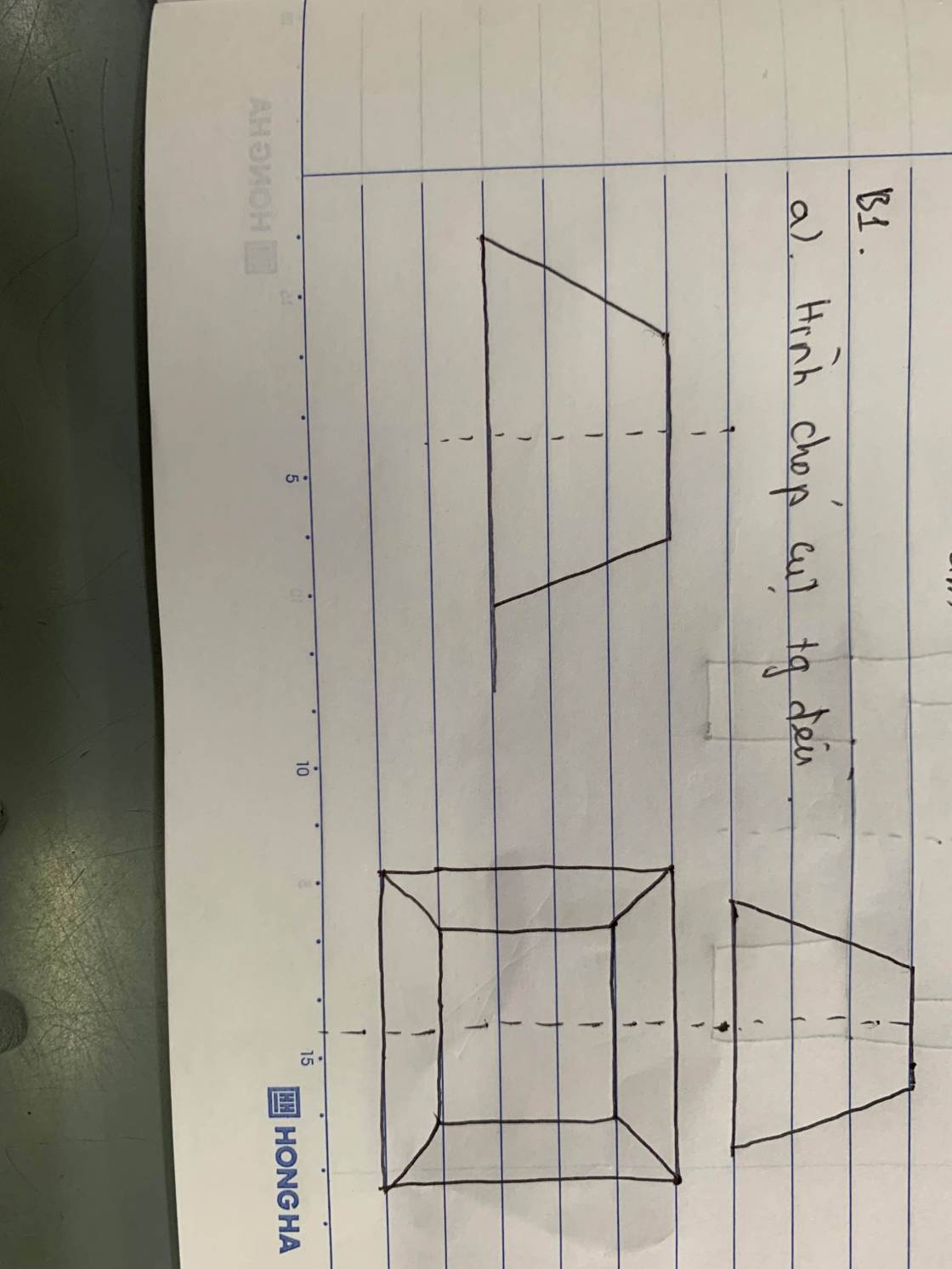
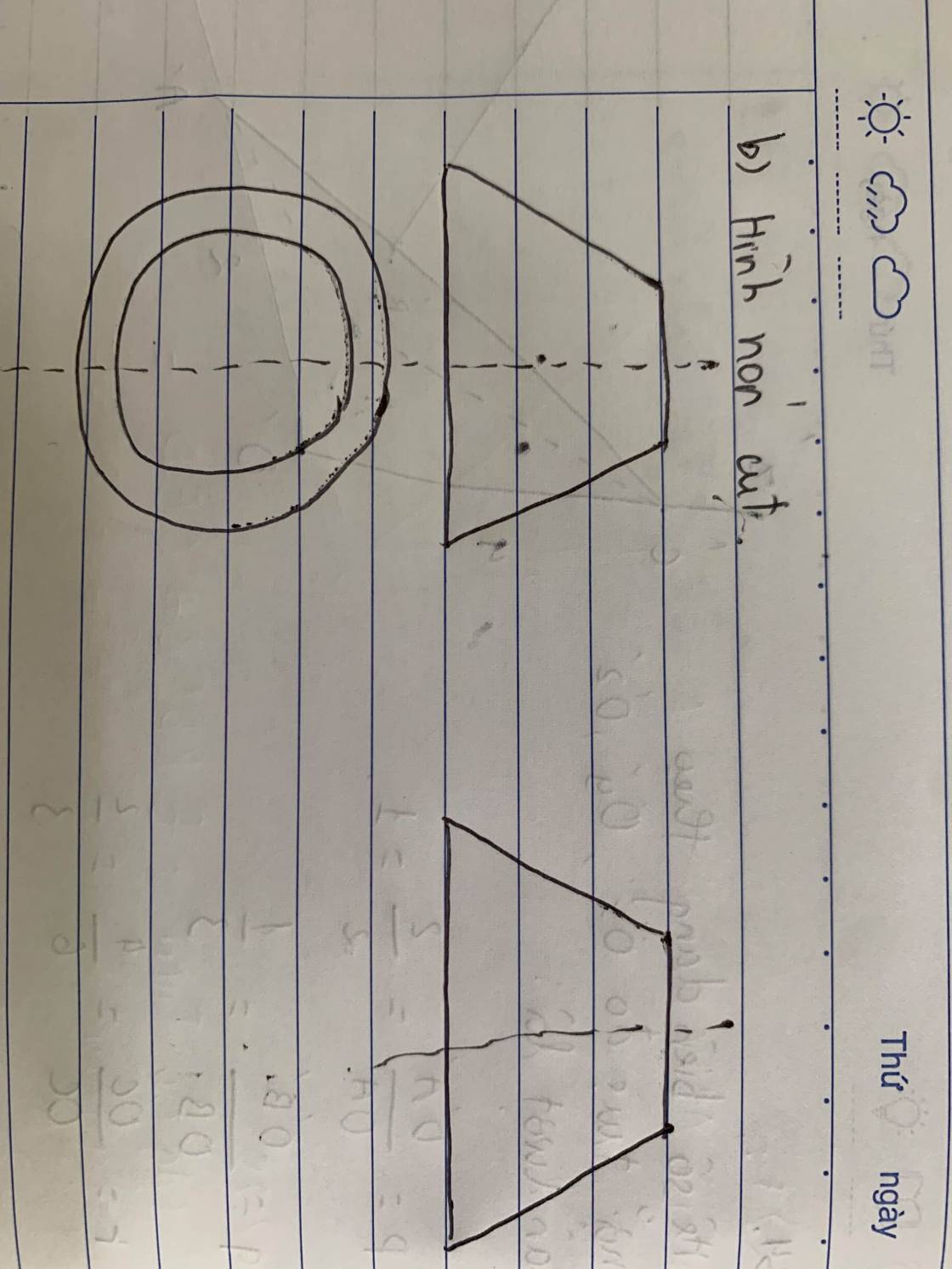
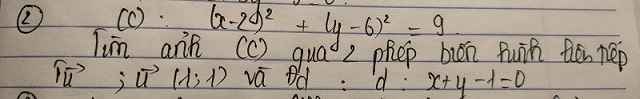



a.
Do chóp S.ABCD đều \(\Rightarrow SO\perp\left(ABCD\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) O là hình chiếu vuông góc của S lên (ABCD)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta OAB\) là hình chiếu vuông góc của \(\Delta SAB\) lên (ABCD)
b.
Gọi E là trung điểm CD \(\Rightarrow OE\) là đường trung bình tam giác BCD
\(\Rightarrow OE||BC\Rightarrow OE\perp CD\)
\(\Rightarrow CD\perp\left(SOE\right)\)
Trong mp (SOE), từ O kẻ \(OK\perp SE\)
\(OK\in\left(SOE\right)\Rightarrow CD\perp OK\)
\(\Rightarrow OK\perp\left(SCD\right)\)
Trong mp (ACK), qua A kẻ đường thẳng song song OK cắt CK kéo dài tại H
\(\Rightarrow AH\perp\left(SCD\right)\Rightarrow SH\) là hình chiếu vuông góc của SA lên (SCD)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{ASH}\) là góc giữa SA và (SCD) hay \(\widehat{ASH}=\varphi\)
\(OE=\dfrac{1}{2}BC=\dfrac{a}{2}\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông SOE:
\(OK=\dfrac{SO.OE}{\sqrt{SO^2+OE^2}}=\dfrac{a\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
O là trung điểm AC và \(OK||SH\Rightarrow OK\) là đường trung bình tam giác CAH
\(\Rightarrow AH=2OK=\dfrac{2a\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
\(OA=\dfrac{1}{2}AC=\dfrac{a\sqrt{2}}{2}\Rightarrow SA=\sqrt{SO^2+OA^2}=\dfrac{a\sqrt{6}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow sin\varphi=\dfrac{AH}{SA}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{30}}{15}\)